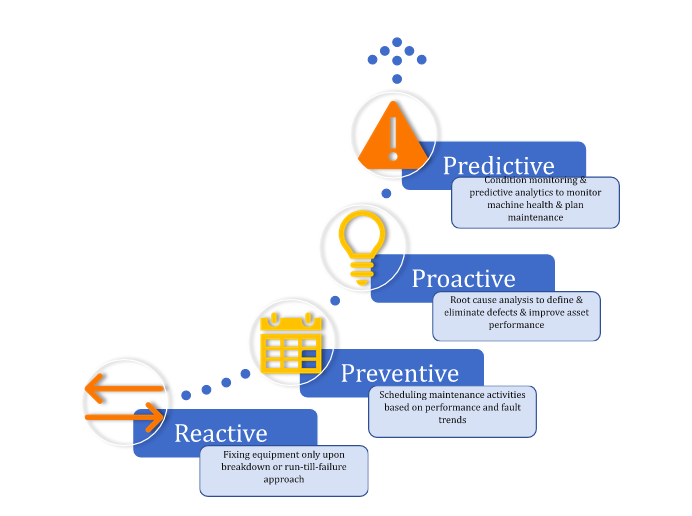
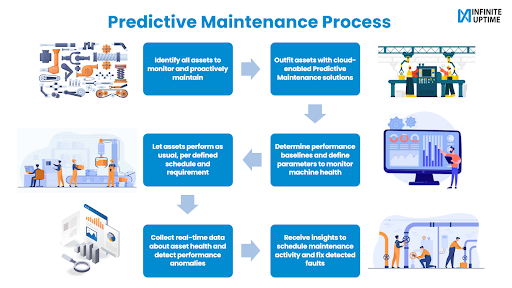
Predictive Maintenance: Is it the best approach for Greenfield or Brownfield projects?

Digital transformation in the industry entails the creation of connected enterprises wherein machines and people can seamlessly communicate and access relevant information in real time. Intelligently digitized factories are able to achieve plant reliability objectives while maximizing production uptime and maintaining optimal machine health. Where the application of smart automation, robotics, the internet of things (IoT), machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) can make this strategically possible in new manufacturing sites, legacy sites often struggle to digitalize key operations.
This evokes the question for many plant and maintenance leaders – is IoT-enabled Predictive Maintenance (PdM) suitable for greenfield (new) projects only or can brownfield (old) projects also successfully adopt it? This article will address this question and deliberate on the suitability of predictive maintenance in both greenfield and brownfield projects.
Predictive Maintenance in Greenfield Projects

To begin with, greenfield projects often have the advantage of factoring in scalable automation and digitalising processes from the off-set. The project plan accounts for such technologies and shop-floor teams are sensitized from the very beginning about the standard digitalized practices. Furthermore, there are no legacy applications to upgrade or distributed assets to integrate, calling for extensive change management.
This makes it easy for plant and maintenance heads to pursue and achieve plant reliability objectives in brand-new manufacturing sites. A digitally transformed production unit can have:
- All machines equipped with sensors or integrated chips to monitor ongoing operations
- Real-time information about asset availability and reliability, accessible through intelligent dashboards
- Sophisticated data storage and big data analytics to generate strategic insights
- Established standard operating procedures (SOPs) to manage digitalized equipment with minimal manual intervention
- Blanket adoption of industrial IoT, AI and machine learning (ML) enabled technologies to support production and maintenance functions
- Safer work environments with minimal equipment breakdown and unplanned downtime
Greenfield projects also need to prioritise asset maintenance and reliability to ensure that such ideal manufacturing conditions are maintained as the production site matures. A predictive maintenance approach becomes a natural fit and can be easily adopted by:
- Outfitting all mission-critical assets for real-time condition monitoring
- Creating digital twins for all equipment; covering as-designed, as-built, and as-maintained states of the assets
- Using machine models and simulations to test out OEM investigation and maintenance strategies
- Utilizing quality data inputs to generate analytical insights about machine health and performance
- Access prescriptive maintenance actions formulated by ML across the connected enterprise
- Continuously support plant-wide asset improvement, while maintaining high safety standards and minimal human intervention
While all these adaptations and benefits are possible in greenfield projects with the right investment and strategy, brownfield projects can go through a completely different process before transformative digitalization can happen.
Predictive Maintenance in Brownfield Projects
Brownfield projects are often decades old and are typically part of process manufacturing. This means that they run 24×7 and even an hour of downtime can mean thousands of dollars lost in revenue. Halting production in such sites to retrofit legacy equipment with IoT-enabled predictive maintenance and digital reliability solutions poses a big challenge.
Moreover, the need for digitization is often realized in critical applications before it’s scaled up to all assets. Such phased digitalization creates an ecosystem of software and hardware that is not necessarily synchronized or can be integrated to generate data-backed intelligence. Manual data collection about machine conditions remains a prevalent practice and is conducted by a third-party condition monitoring partner or an in-house CBM team. These teams are also resistant to the adoption of new technology, fearing the obsolescence of their roles.

All these challenges are compounded by the high cost of retrofitting legacy equipment with the latest technologies and discourage plant heads from actively pursuing more advanced monitoring, diagnostic, maintenance, and asset management solutions. But all is not lost! Brownfield projects can derive greenfield benefits from intelligent automation and a predictive maintenance approach by:
- Adopting holistic and scalable digital reliability solutions that can be integrated with the existing CRM and OT/IT infrastructure
- Digitizing critical applications with advanced diagnostic and monitoring sensors to receive real-time information about machine condition
- Automating information flow and generating analytical intelligence to support maintenance activities, thus minimizing production downtime
- Training operations and maintenance teams to utilize predictive analytics and prescribed actions before performing OEM investigations and/or replacement of components
- Pivoting from a preventive maintenance approach towards a predictive maintenance approach to extend the remaining useful life (RUL) of assets and optimize production uptime
- Determining ROI of digitalization not only in terms of costs saved or downtime avoided but also safer and more sustainable production environment created.
Final Thoughts
In sum, predictive maintenance, digital reliability, and other industry 4.0 technologies are not just limited to greenfield projects. They could be equally, if not more, relevant for brownfield projects operating with older equipment and outdated asset management processes. With the right management outlook, a digitalisation strategy can be devised for old manufacturing sites and systematic automation can be done to optimize production and maintenance processes.
Infinite Uptime’s digital reliability solutions are designed to understand the very specific maintenance needs of process manufacturing plants with crucial assets running uninterrupted for many decades. Tailored monitoring insights and predictive analytics are shared with plant leaders in industries such as Cement, Steel, Mining, Automotive, Tyre, Chemicals, Paper, FMCG, Pharmaceuticals, Glass, Oil & Gas, etc. Our patented vibration analysis technology and syndicated reliability reports allow maintenance leaders in brownfield projects to derive greenfield projects and maximize their plant reliability.
Get in touch with our experts or book a demo now to understand how our solutions fit your plant.