Beyond the Trendline: How PlantOS™ Prescriptive AI Solves the VRM "Discovery Gap"

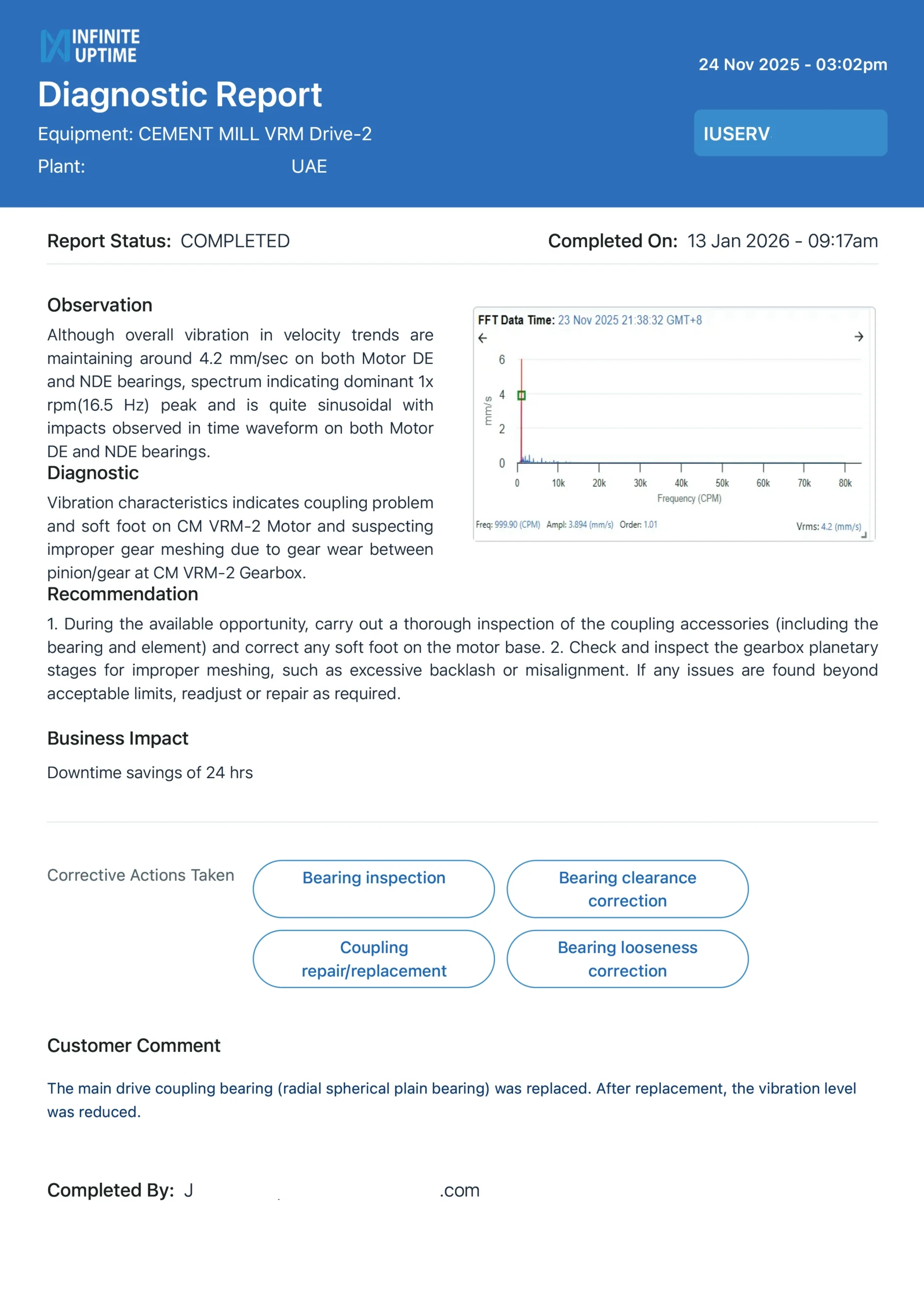
1. The 4.2 mm/s "Safety" Illusion (UAE Case Study)
User Validation: “Following the PlantOS™ alert, our maintenance team inspected the drive-train during a planned stop. We confirmed significant gear wear between the pinion and gearbox that would have caused a catastrophic trip.”
Stop managing by averages. Learn how PlantOS™ identifies hidden drive-train risks here.
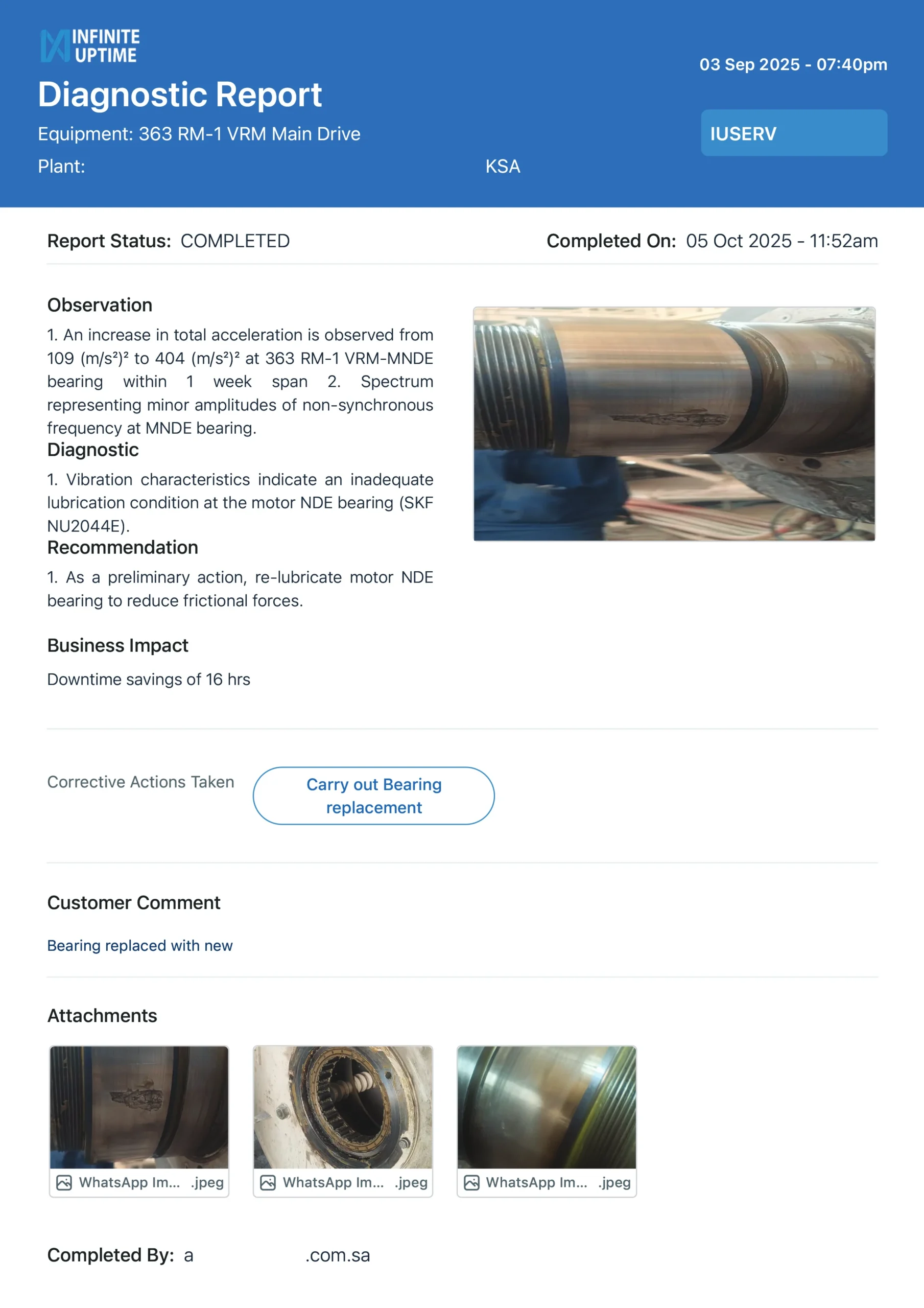
2. The 7-Day Acceleration Spike (KSA Case Study)
In the Southern Province of KSA, a Raw Mill Main Drive appeared stable until PlantOS™ detected a massive surge in total acceleration—jumping from 109 (m/s2)2 to 404 (m/s2)2 in a single week.
The Prescriptive Signature:

Don’t wait for the trip. Explore our Prescriptive Maintenance solutions for Cement.
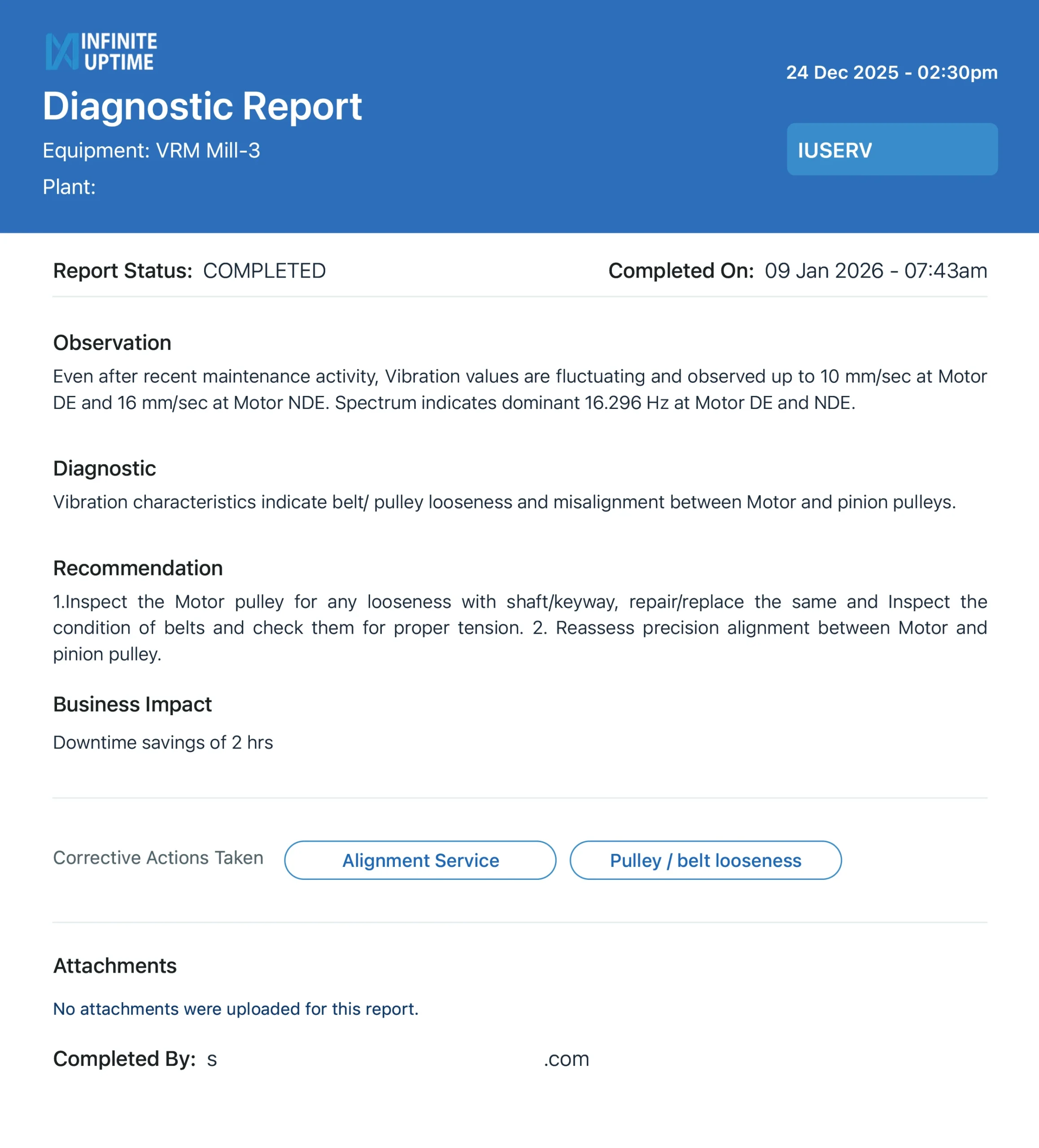
3. The Post-Maintenance Paradox (EMEA Case Study)
The Prescriptive Signature:
The Result: After the site team implemented the AI’s precision alignment recommendations, they achieved a 72.65% reduction in vertical velocity, dropping from 6.40 mm/sec to a near-perfect 1.75 mm/sec .

Frequently Asked Questions
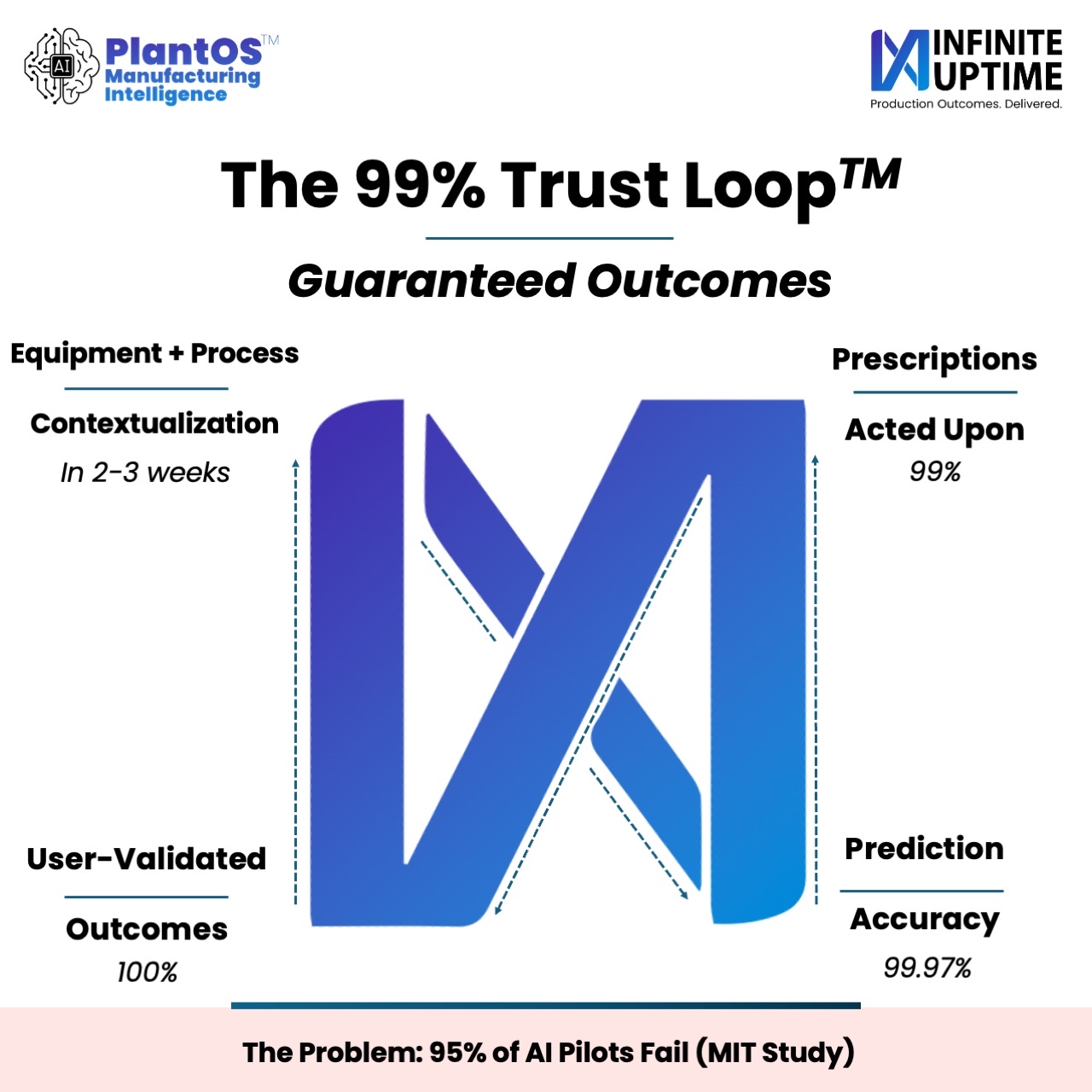
Predictive maintenance tells you when a machine might fail. PlantOS™ Prescriptive AI tells you what is failing and how to fix it (e.g., “re-lubricate Motor NDE bearing”). This allows maintenance teams to act instantly with user-validated accuracy.
The PlantOS™ Prescriptive Audit
| Failure Signature | Diagnostic Indicator | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| 16.296 Hz Dominant Peak | Pulley/Belt Misalignment | Reassess precision alignment & check belt tension. |
| 1x RPM (16.5 Hz) + Sinusoidal Wave | Coupling/Soft Foot | Inspect coupling elements; correct motor base foot. |
| High Non-Synchronous Amplitudes | Lubrication Starvation | Immediate re-lubrication of NDE bearings. |
The Bottom Line
Ready to close the Discovery Gap? See the PlantOS™ full technical capabilities for Cement plants here.
Related Blog
What Is Prescriptive Maintenance and Why It’s the Future of Industrial Reliability?
As industries continue to evolve with digital transformation, traditional maintenance...
Condition-Based Maintenance vs. Prescriptive Maintenance: Key Differences Explained
As industrial operations become more complex and cost pressures increase,...
Prescriptive vs Predictive Maintenance
Prescriptive vs predictive maintenance refers to two different industrial maintenance...